1. What is urticaria?
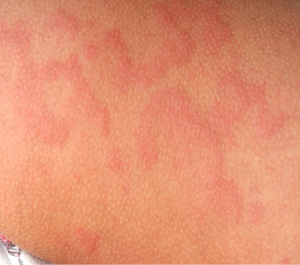
Urticaria's is localized itchy, pink wheals (swellings) that may occur singularly or in groups on any part of the skin; they are part of an allergic reaction. Approximately 10-20 percent of the population will have at least one episode in their lifetime. Most episodes of hives disappear quickly in a few days to a few weeks. When hives form around the eyes, lips, or genitals, the tissue may swell excessively. Although frightening, the swelling usually goes away in less than 24 hours. Severe cases of hives may cause difficulty in breathing or swallowing and emergency room care is required.
2. What causes urticaria?
Urticaria can be caused by some of reasons including Foods, Drugs, Infections, Endocrine, Abnormalities or Systemic illness.
-
Foods : The most common foods that cause urticaria are: nuts, chocolate, shellfish, tomatoes, eggs, berries, and milk. Fresh foods cause hives more often than cooked foods. Food additives and preservatives may also cause hives. Hives may appear within minutes to several hours after eating, depending upon the site within the digestive tract where the food is absorbed.
-
Drugs : Almost any medication can cause hives. Antibiotics, pain medications, sedatives, tranquilizers, diuretics (water pills), diet supplements, antacids, arthritis medication, vitamins, herbal supplements, eye and eardrops, laxatives, vaginal douches, or any other non-prescription item can be a potential cause of urticaria. It is important to inform the dermatologist of ALL prescription and over-the-counter medications being used to help find the cause of the hives.
-
Infections : Many infections can cause urticaria. Viral upper-respiratory tract infections (colds) are a comon cause in children. Other viruses, including hepatitis and a number of bacterial and fungal infections, may cause urticaria.
Most of the patients have coexisting thyroid abnormality. Urticaria can also be manifestation of any systemic illness including malignancy.
3. What is angioedema?
It is a condition characterized by the sudden & temporary appearance of large areas of swelling in the subcutaneous tissue (layer below the skin) or submucosa, with or without hives. In severe cases there can be difficulty in breathing, abdominal pain if the internal organs are involved. This can be life threatening and the patient has to be taken to the hospital immediately.
4. What is the treatment for urticaria?
The best treatment for urticaria is to find and eliminate the cause whenever possible. Antihistamines are prescribed to provide relief and work best if taken on a regular schedule to prevent hives from forming. There are many antihistamines available. No one antihistamine works for everyone. The dermatologist may use combinations to control the urticaria. In severe cases, an injection of epinephrine (adrenalin) may be needed. Cortisone may also bring dramatic relief, but its use must be limited to short periods of time.