1. What is hirsutism?
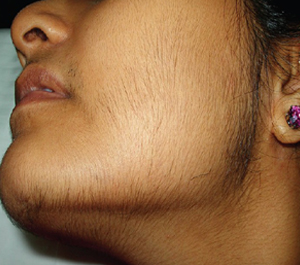
Hirsutism is defined as the excessive growth of thick dark hair in an androgen-dependent pattern (male pattern) where hair growth in women is usually minimal or absent like the face, chest, and areolae. It occurs as a result of increased androgen production, increased skin sensitivity to androgens, or both.
2. What causes hirsutism?
Increased androgen levels in females can be due to increased production either by the adrenals or due to an ovarian disease. The ovarian causes for hyperandrogenism are polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) and ovarian tumors. Adrenal causes include Cushing's syndrome, androgen-producing tumors, and congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH),. Other endocrine abnormality that causes hirsutism include hypothyroidism and increased prolactin levels.
About 20% of the patients may present with idiopathic hirsutism with normal androgen levels and ovarian function. The cause of increased hair in these women is thought to be related to disorders in peripheral androgen activity. Hirsutism can also occur in some women after menopause. This is due to decrease in ovarian estrogen secretion with continuous androgen production. Hirsutism may be familiar with genetic predisposition or may be related to stress. Many medications can also cause hirsutism.
3. What is the treatment of hirsutism?
Mild hirsutism usually may not require treatment, unless patient is psychologically disturbed. Hirsutism that is associated with irregular menstrual periods or hormonal imbalance requires medical intervention together with cosmetic treatment. Topical cosmetic therapies like Shaving, threading, waxing, using depilatory creams, electrolysis may not be useful in all patients.
Laser hair reduction - Laser hair reduction can treat larger areas, it is painless and no anesthesia is required. Is most effective on dark hairs in fair-skinned people. Multiple treatments may be necessary for long-term hair destruction.